
-
 About Us
About Us Detailed information about Zonguldak Coal Geopark and more...
About Us
About Us Detailed information about Zonguldak Coal Geopark and more... -
 Enjoy
Enjoy
-
 Discover
Discover Discover Zonguldak Geoparks
Discover
Discover Discover Zonguldak Geoparks -
 Learn
Learn
-
 Activities
Activities
-
 GeoNetwork
GeoNetwork
-
 Contact Us
Contact Us
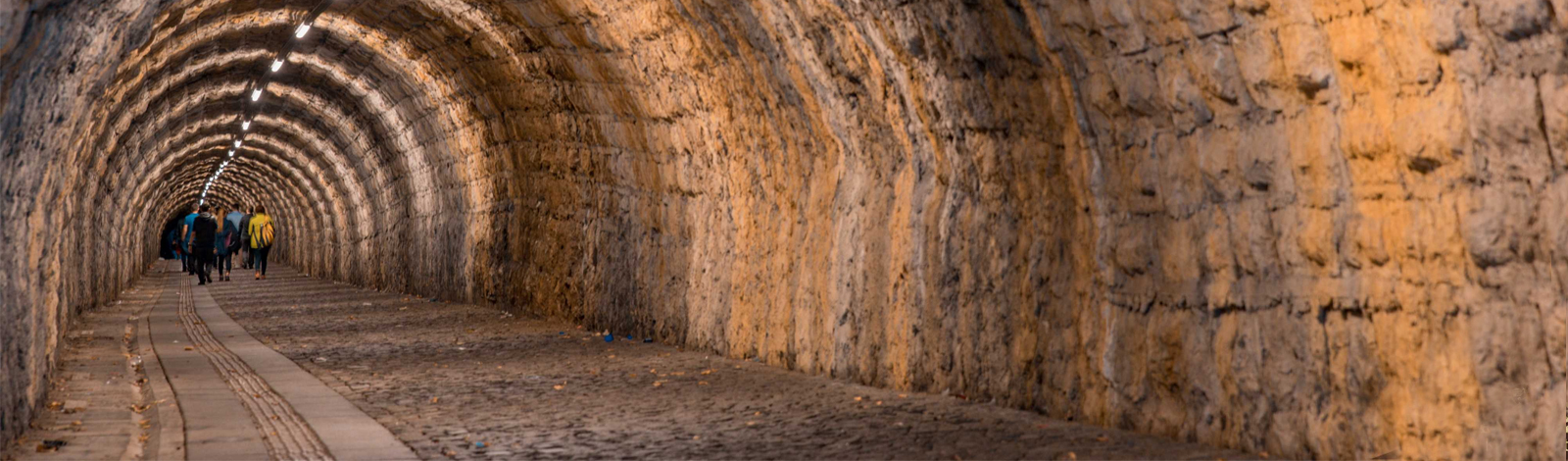


Frequently Asked Questions
What is Geopark?
The concept of "Geopark" emerged with a declaration signed by more than 100 participants from more than 30 countries during the First International Symposium on Conservation of Geological Heritage held in Digne, France in 1991.
Geoparks; It is the field of disaster preparedness and geological awareness for geological hazards such as volcanoes, tsunamis and earthquakes. They are places where climate change information is stored. Geoparks are areas where geological and natural beauties are preserved and transferred to future generations, and the history of the earth is learned through geotourism in these areas. Elements that explain the formation of the earth's crust, representatives of a known event, rare or very large formations are defined as geological heritage. Geoparks are special nature protection areas with planned management, where different or the same type of geological heritage samples of international importance coexist.
Contributing to the protection of nature and geological heritage and the development of nature tourism; arranging natural areas with rare, aesthetic, scientific and economically valuable geological, geoformological, biological and cultural heritage elements for educational, tourism and economic purposes; They are geographical areas with certain borders that provide the promotion of the region to the whole world and contribute to local development.
Geoparks are conservation areas that aim to preserve geosites and transfer them to future generations; At the same time, it is a sustainable development area that aims the social and cultural development of the local people. It is defined as the areas where the same or different types of geosites are found collectively, not less than the pedestrian walking distance.
What is Geosite?
It is a rock, mineral, fossil assemblage, structure, stack, landform or piece of land that expresses any current or ancient geological process, event or feature. Those with archaeological or historical value are called cultural geosites.
What is Geological Heritage?
A geosite of significant scientific or visual value, threatened by natural or man-made extinction.
What is the UNESCO Global Geopark Network?
UNESCO; It started to work with geoparks in 2001 and it was decided to create a Global Geopark Network in 2004. As of 2021, there are 177 Geoparks from 46 countries that have completed their international registration in the UNESCO Global Geopark Network.
In our country, only Kula-Salihli Geopark located in Manisa has been accepted as a member of UNESCO Global Geopark.
Click the link below for detailed information.
What is Geotourism?
Geotourism, a new concept of nature tourism born in geoparks, refers to travels to natural environments to see and recognize geological and geomorphological formations. It is a nature friendly tourism type and is an important resource for sustainable local development. For the first time, the socio-economic development of the local people in the protected area was defined as a priority with the concept of Geopark and Geotourism. While before the geoparks, human and human activities were excluded from the protected areas, for the first time, the geoparks accepted them as a natural and inseparable part of the protected area. Geoparks not only accept economic activities in the protected area, but also encourage local entrepreneurs and support existing businesses to diversify and make them more efficient. In particular, they accept the development of tourism-related products and services as the development axis of the Geopark, and as the Geoparks develop, they also develop the local people in their areas through Geotourism. The United Nations declared 2017 the "International Year of Sustainable Tourism Development" and UNESCO Geoparks was selected as the only privileged partner of this program.
What is Geo-Education?
Each geopark organizes activities in order to convey concepts related to earth sciences and environment to the society. Geoparks; It aims to create a basic level of love for nature and environmental awareness in society, especially children and youth. A livable world, sustainable prosperity and future world will be possible by living in peace and harmony. It is not possible to live in harmony with the earth without understanding the earth and its dynamics. For this reason, Geoparks see nature as a library and reduce its language to the language of ordinary people. Geoparks; With guided tours, Geopark Natural History Museums, educational materials, it deals with making the story of the earth interesting, meaningful and understandable for ordinary people, and this whole process is characterized as Geo-education.
What is Geo-Conservation and Sustainability?
Each geopark researches and applies new methods to perfectly protect important geological formations. Geological or geomorphological formations that are important in geoparks are accepted as a unique heritage of the earth and it is the responsibility of Geoparks to take all necessary precautions and to carry out studies so that this valuable information resource reaches future generations. There are two types of protection in geoparks, the first of which is "Protection", which covers all kinds of legal measures to protect the site heritage, the activities of security guards called "Park Rangers"; “Conservation”, on the other hand, refers to all kinds of chemical, physical and laboratory practices aimed at protecting, improving and restoring the land heritage, especially fossils. Effective protection in the geopark is possible with a balanced application of these two parameters.
What is Geodiversity?