-
 About Us
About Us Detailed information about Zonguldak Coal Geopark and more...
About Us
About Us Detailed information about Zonguldak Coal Geopark and more... -
 Enjoy
Enjoy
-
 Discover
Discover Discover Zonguldak Geoparks
Discover
Discover Discover Zonguldak Geoparks -
 Learn
Learn
-
 Activities
Activities
-
 GeoNetwork
GeoNetwork
-
 Contact Us
Contact Us
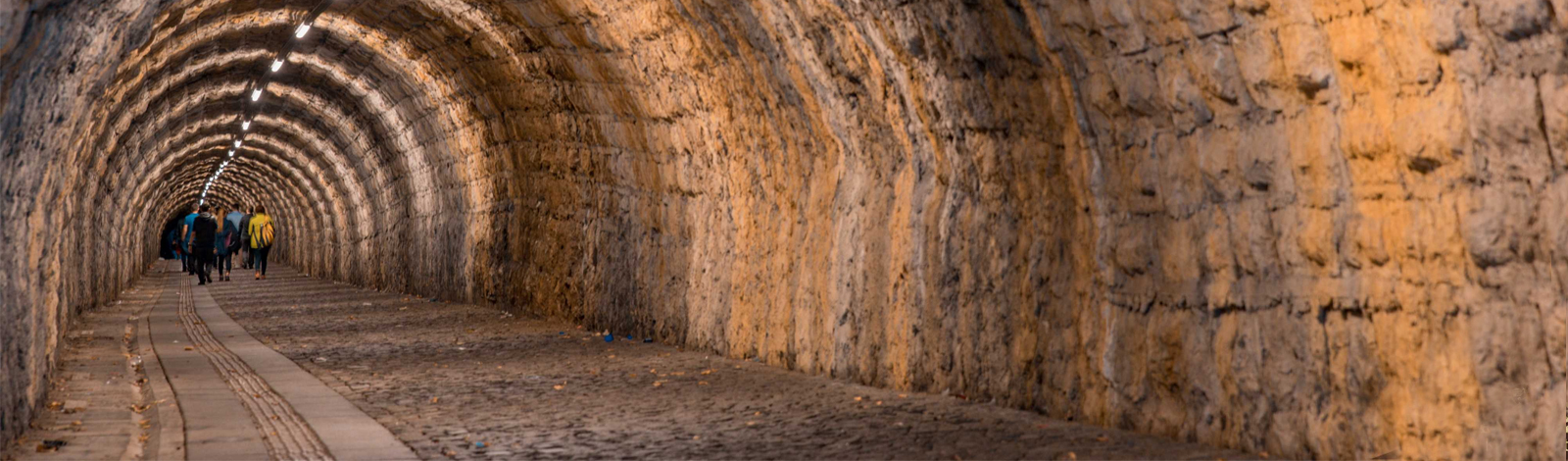


Geological Heritage
Carboniferous Forests
Carboniferous Forests; It was formed by plants dependent on water and moisture in the equatorial belt of Pangea (the landmass that was further north when the continents on Earth were together as a single continent before taking their present positions) and in the swampy environments of the ocean near the abundant rainfall. The arid interiors of the Pangea continent were thus covered with much lesser vegetation or deserts. Gondwana continent, which is close to the south pole, had a cold and unique vegetation. The Carboniferous Forests were formed when the plant groups that emerged in the last part of the 1st Time (Paleozoic) Devonian (the period before the Carboniferous) and extending from the ocean edges to the interior parts covered the land along the equatorial belt during the Carboniferous period. Therefore, despite the presence of coal deposits in Late Devonian rocks, most of the oldest coal reserves on Earth were formed during the Carboniferous period.
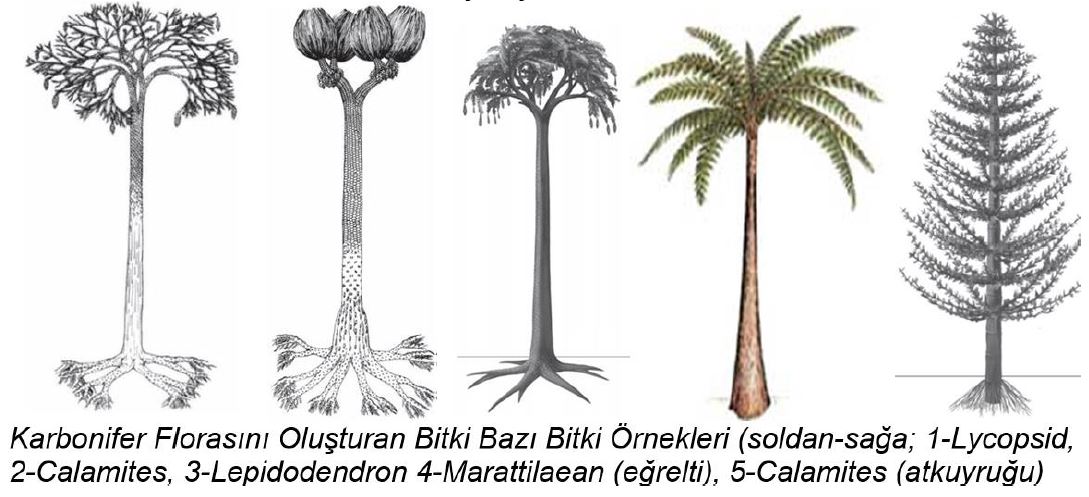
No new plant species emerged during the Carboniferous period, but in the last part of the Devonian, plants evolved and reached even larger sizes. The presence of plant fossils, mostly reaching 10 meters in length, in the coal basins formed during the Carboniferous period is shown as evidence for this assessment. Since the plants in the Carboniferous period were simpler than the plants of today; their leaves were small, their trunks did not develop a woody structure (the outer shell that provides structural support by compressing the base and branches) and because they could not pass the flowering stage (flowering plants emerged 140 million years after the Carboniferous in the Jurassic period).
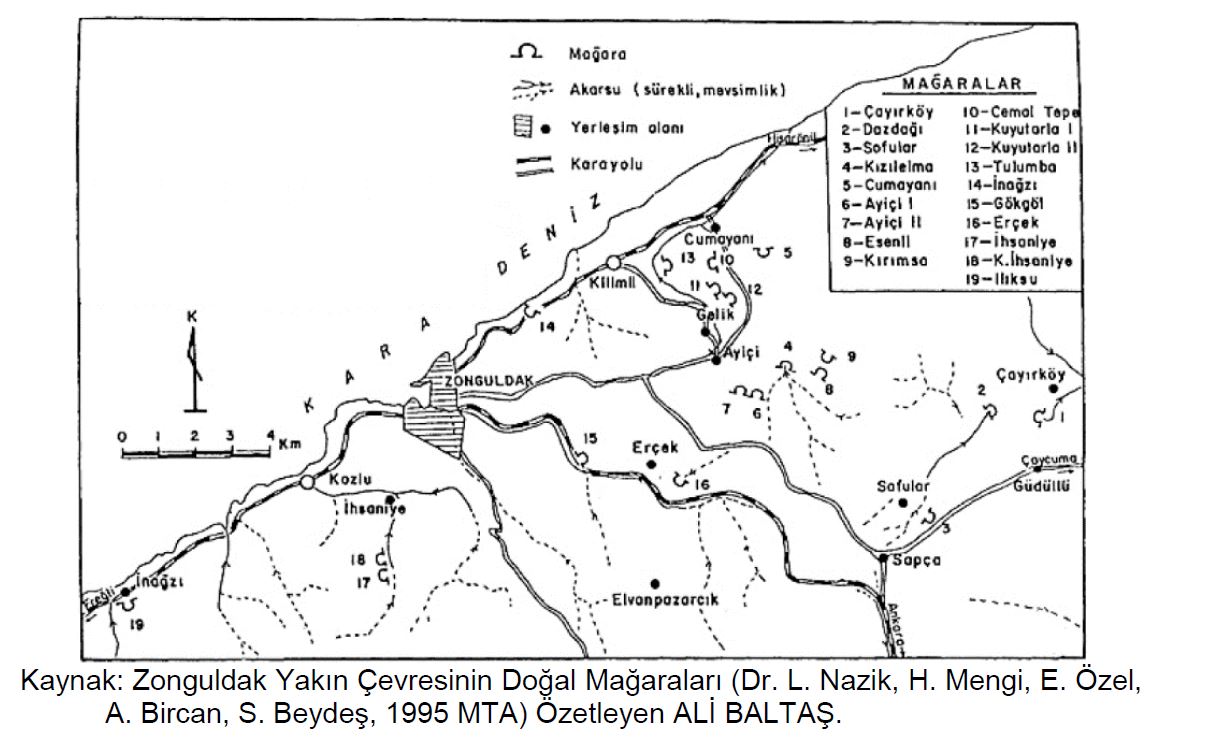
Zonguldak Caves
Some of the caves in the vicinity of Zonguldak are in the Yılanlı Formation (Vizeeen, 347-330 million years) located at the base of the Upper Carboniferous (Namurian-Westphalian, 330-300 million years) aged coal-bearing formations, and some of them are unconformably at the ceiling of the Upper Carboniferous coal-bearing formations. They were developed in the Zonguldak Formation (Barremian, 129-125 million years) and Kapuz Formation (Apsian, 125-113 million years), which are geologically lost periods. The time intervals given here are not the age of the caves, but the time period in which the rocks were formed, that is, the age of the rocks. Caves in the Zonguldak Region began to form from the Pliocene (5-2 million years) period after Anatolia gained its current position and climate characteristics as a result of continental movements.
Caves Developed in Yılanlı Formation (Vizeen, 347-330 million years) at the Base of Coal Formations;
Clam Pits
Cayirkoy Cave
Dazdagi Sinkhole (Sinkhole; closed pit of different diameters and depths, natural well)
Ascetic Cave
Gokgol Cave
Ercek Cave
İhsaniye Caves
Caves Developed in Zonguldak and Kapuz Formation Found on the Ceiling of Coal Formations
Caves Developed in the Zonguldak Formation (Barremian, 129-125 million years ago)
Ayiçi I Sinkhole
Ayiçi II Sinkhole
Red Apple Cave
Cemaltepe Sinkhole
Kuyutarla I Cave
Kuyutarla II Cave
Tulumba Cave
Iliksu Cave
Caves Developed in the Kapuz Formation (Aptian, 125-113 million years ago)
Cumayani Cave
Esenli Sinkhole
Krimsa Sinkhole
Inagzi Cave